Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases in the world, and its prevalence continues to increase. It is characterized by high blood glucose levels, which can have serious health consequences if not managed properly.
In this article, we'll explore what diabetes is, how it relates to high glucose levels, the consequences of not controlling it, and how people can use technologies and apps to manage their diabetes more effectively.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic condition that occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively.
Insulin is a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar (glucose). When not enough insulin is produced or the body cannot use it properly, blood glucose levels rise.
There are several types of diabetes, but the most common are type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes
This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in young people, as it is an autoimmune disease that destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes depend on external insulin to control their glucose levels.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is most common and usually develops in adults, although it is also increasing in younger people due to rising obesity and unhealthy lifestyle habits.
In this case, the body does not use insulin efficiently or does not produce enough, causing an increase in blood glucose levels.
Why are blood glucose levels important?
Blood glucose levels are a key indicator of metabolic health. Glucose is the body's primary source of energy, and insulin helps cells absorb this energy.
When blood glucose levels are too high, damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs can occur. This is why diabetes must be properly managed to prevent serious complications.
Consequences of high glucose levels
High blood glucose levels can have several short- and long-term consequences. If left uncontrolled, they can lead to serious complications affecting various parts of the body.
1. Damage to blood vessels
High glucose levels damage blood vessel walls over time. This can lead to circulatory problems, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral vascular disease.
2. Kidney damage
The kidneys are very sensitive to the effects of high glucose. Prolonged damage to the kidney's blood vessels can result in kidney failure, which may require dialysis or even a kidney transplant.
3. Neuropathy
Excess glucose also affects the nerves, especially in the extremities. This can cause pain, numbness, and circulation problems in the hands and feet. In severe cases, diabetic neuropathy can lead to amputation.
4. Eye problems
Uncontrolled diabetes is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults. Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes can cause vision problems such as diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma.
5. Heart disease
People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing heart disease due to the effects of high glucose on blood vessels and increased blood pressure. This can lead to heart attacks, heart failure, and other cardiovascular problems.
6. Reduced immunity
Diabetes also affects the immune system, making people more susceptible to infections. Wounds may take longer to heal, and infections can spread quickly if not properly controlled.
See Also:
- Apps to Detect Impurities in the Air
- Free Apps to Learn English
- Apps to Try Beard Styles
- The best music recognition apps
- Apps to Block Fraud Calls
How to control glucose and manage diabetes?
Glucose control is essential to prevent complications associated with diabetes. Appropriate treatment depends on the type of diabetes and each individual's personal habits.
However, there are several ways to control glucose and manage diabetes effectively.
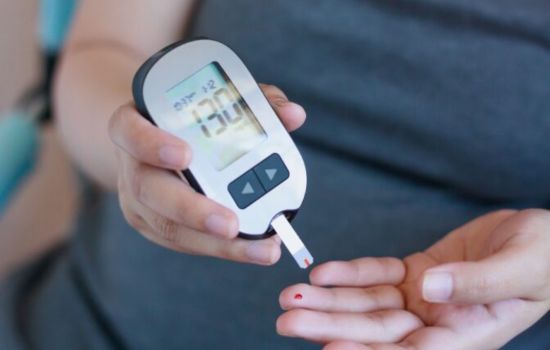
1. Regular monitoring of glucose levels
A fundamental part of diabetes management is regularly monitoring blood glucose levels. This allows people with diabetes to adjust their diet, exercise, and medication as needed.
Frequent measurements help keep glucose levels within the recommended range.
2. Balanced diet
A healthy diet is key to controlling glucose levels. People with diabetes should focus on eating fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, and avoid refined carbohydrates and sugars. It's also important to eat portion-controlled meals and follow a regular meal schedule.
3. Regular exercise
Exercise is a vital component of diabetes management. It helps reduce blood glucose, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy body weight.
It is recommended to do at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
4. Medication
For people with type 1 diabetes, insulin is essential for controlling glucose levels. For people with type 2 diabetes, oral medications or insulin may be necessary to control glucose.
It is important to follow your doctor's instructions to take your medication correctly.
5. Stress management
Stress can affect blood glucose levels, so it's important to find effective ways to manage it. Relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help reduce stress and improve glucose control.
Using Glucose Monitoring Apps: Technology for Managing Diabetes
With the advanced technology available today, there are many apps that can help people monitor their glucose levels and manage their diabetes more effectively.
One of the best apps available is the glucose monitoring app, which can help track levels, detect patterns, and provide useful information.
1. Glucose Monitoring: The Importance of Accuracy
Constant monitoring of glucose levels is essential for making informed decisions about medication, diet, and exercise.
Mobile apps, such as the glucose monitoring app, allow users to enter their glucose levels, track trends, and receive personalized recommendations.
2. Benefits of diabetes apps
Diabetes apps allow for more accessible and consistent monitoring. They can also integrate with other monitoring devices, such as glucose meters, and keep detailed records, making it easier for healthcare professionals to review results.
Additionally, these apps can send reminders about glucose monitoring, medication intake, and physical activity, helping users stay on track.
3. Glucose Monitoring App: Features
The glucose monitoring app is easy to use, with a user-friendly and easy-to-navigate interface. Users can record their blood glucose levels several times a day, view trend graphs, and receive tips on how to manage their levels.
The app can also store information about medications, meals, and activities, providing a complete view of the user's overall health.
4. Personalized advice and recommendations
One of the best features of these apps is the ability to receive personalized recommendations based on the data you enter.
For example, if glucose levels are outside the recommended range, the app may suggest dietary or exercise changes to help stabilize levels.
In addition, apps often include tips on how to improve overall health and keep diabetes under control.
5. Monitoring and analysis
Data tracking and analysis is a key feature of diabetes apps. Users can gain detailed insights into how their eating habits, activity levels, and medications affect their glucose levels.
This information is useful for both users and healthcare professionals, as it allows for more precise adjustments to treatments and recommendations.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic disease that requires constant management to avoid serious complications. Monitoring glucose levels, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking appropriate medications are key aspects of managing diabetes.
By using mobile apps, such as the glucose monitoring app, people with diabetes can keep more accurate and efficient track of their health.
By using these apps, users can receive reminders, get personalized recommendations, and track their progress consistently.
Without a doubt, technology plays a crucial role in diabetes management, providing useful tools to improve the quality of life of those affected.
It is important, however, for people with diabetes to work closely with their doctors to ensure their glucose levels remain within the recommended range and prevent long-term complications.